Ethical Data Collection for CRO

Ethical Data Collection for CRO
 27-01-2026 (Last modified: 27-01-2026)
27-01-2026 (Last modified: 27-01-2026)
Ethical data collection ensures user privacy while improving Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO). The focus is on three principles: transparency, accountability, and data minimization. By being clear about what data is collected, why it’s needed, and how it’s used, businesses can build trust, comply with laws like GDPR and CCPA, and enhance user experiences.
Key Takeaways:
- Consent First: Always get explicit user consent before tracking.
- Minimize Data: Collect only what’s essential, like click patterns or checkout progress.
- Anonymize Data: Remove personal identifiers early to protect user privacy.
- Transparency: Use simple language to explain data usage and provide opt-out options.
- Compliance: Follow GDPR and CCPA rules to avoid fines and legal risks.
- Regular Audits: Review data practices annually to ensure ethical standards.
Why It Matters:
Unethical practices damage trust and lead to legal consequences. For example, GDPR fines reached €5.88 billion by 2025. Ethical approaches, like transparent consent systems, improve data quality and user trust – Kmart Australia saw a 200% increase in consenting customers after adopting such methods.
Tools like PageTest.AI help marketers implement ethical CRO strategies by automating compliance, anonymizing data, and offering user-friendly consent options.
Building Ethical Data Practices in Cross-Functional Communities, with Kevin Hartman, Pt 1
Ethical Data Collection Checklist
This checklist takes the ethical principles discussed earlier and turns them into actionable steps for your CRO strategy. Use these guidelines to integrate ethical practices seamlessly into your approach.
1. Obtain Explicit User Consent
Always ensure users actively opt in before tracking their behavior. Use clear, straightforward consent banners that offer equal ease for opting in or out. This concept of "choice symmetry" ensures fairness.
"You must make it as easy for people to refuse consent as it is to accept consent." – Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO)
Simplify the process by using layered notices. Start with a brief summary and provide more details below, such as separating consent for analytics from personalized advertising. For mobile users, keep consent scripts lightweight (under 15KB) to avoid slowing down page load times. You can also implement just-in-time notices that appear only when data collection begins, ensuring users are fully informed before giving permission.
2. Minimize Data Collection
Limit data collection to only what’s necessary for your CRO goals. Instead of gathering excessive information, focus on behavioral triggers like click patterns or checkout progress. Behavioral data often provides better insights into future actions compared to static demographics. For segmentation, group users into aggregated counts – for example, tracking "500 visitors proceeded to checkout" rather than storing individual profiles.
3. Ensure Transparency with Users
Use plain, relatable language to explain how data is handled. Swap technical terms like "third-party affiliates" for clearer phrases like "other companies we work with." Similarly, replace "data processing" with "handling your information". Highlight benefits to users – such as performance cookies speeding up page loads or marketing cookies enabling relevant offers. Display privacy details at data collection points, supported by icons for clarity.
Research shows that organizations with well-designed consent experiences see 40–60% better data completeness. Avoid manipulative designs, as studies found 97% of EU apps used such tactics in 2024, and 83% of users might abandon brands using these methods.
4. Anonymize and Pseudonymize Data
Strip personally identifiable information (PII) from your data at the earliest stage possible. Anonymizing data – such as aggregating user actions instead of tracking individuals – reveals trends without compromising privacy. Pseudonymization, which replaces identifying details with artificial markers, adds another layer of protection. Group users by behavior, like "abandoned cart visitors" or "repeat buyers", without storing details that could trace back to individuals. This aligns with Privacy by Design principles.
5. Comply with Privacy Regulations
Adhering to laws like GDPR and CCPA is non-negotiable. By January 2025, GDPR fines totaled €5.88 billion, showing the importance of compliance. For instance, Meta Platforms was fined €1.2 billion in May 2023 for failing to follow Privacy by Design rules, and Amazon faced a €746 million penalty in July 2021 for unclear consent mechanisms.
GDPR requires specific, detailed consent for each purpose, while CCPA limits data retention to 12 months. Acceptance rates vary – 55–80% for financial services and 45–70% for e-commerce. Supporting universal opt-out tools like Global Privacy Control ensures you respect user preferences.
6. Provide Opt-Out and Data Deletion Options
Give users ongoing control over their data. Offer a persistent, easy-to-access withdrawal option, such as a floating icon or a visible settings menu. Make opting out as simple as opting in. Additionally, provide clear instructions for data deletion so users can have their information removed promptly if they choose to disengage.
7. Conduct Regular Data Audits
Perform data audits at least once a year to ensure your practices meet ethical and legal standards. During these reviews, evaluate the relevance of stored data to your CRO goals and confirm the security of storage methods. Test your consent mechanisms with real users to ensure the language and choices are understandable. Regular audits not only help you stay compliant but also allow you to catch and fix potential issues early.
GDPR vs. CCPA: What You Need to Know
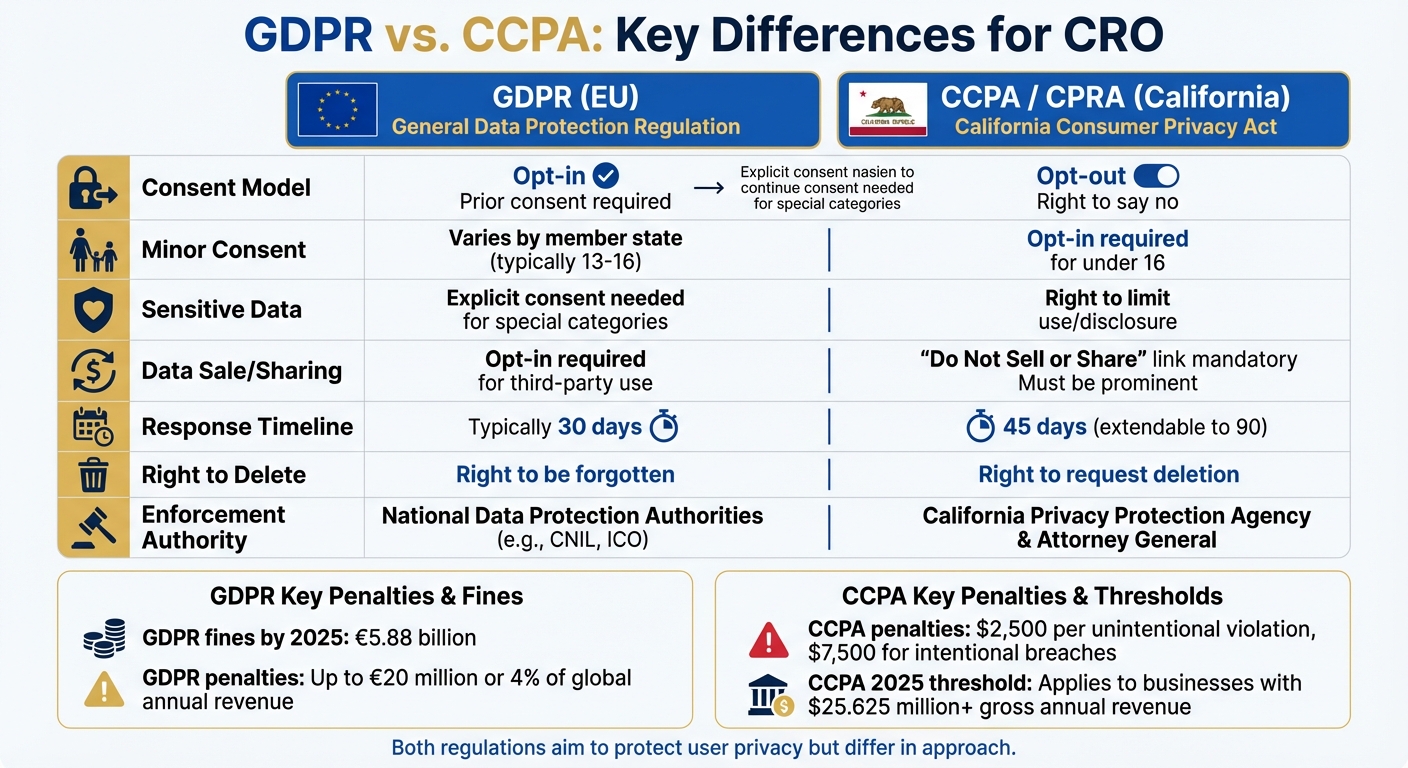
GDPR vs CCPA Privacy Regulations Comparison for CRO
Understanding the nuances between GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is essential for aligning your CRO data practices with the appropriate legal guidelines. While both regulations aim to protect user privacy, they approach consent and enforcement in distinct ways. These differences directly influence how you gather and manage user data for CRO purposes.
Under GDPR, users must provide explicit opt-in consent before data collection begins. In contrast, CCPA assumes consent unless the user actively opts out – except for minors under 16, who require explicit consent.
The penalties also vary significantly. GDPR violations can lead to fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Meanwhile, CCPA penalties range from $2,500 per unintentional violation to $7,500 for intentional breaches . Starting January 1, 2025, CCPA will apply to businesses with gross annual revenues of $25.625 million or more.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of key features:
| Feature | GDPR (EU) | CCPA/CPRA (California) |
|---|---|---|
| Consent Model | Opt-in (prior consent required) | Opt-out (right to say no) |
| Minor Consent | Varies by member state (typically 13–16) | Opt-in required for under 16 |
| Sensitive Data | Explicit consent needed for special categories | Right to limit use/disclosure |
| Data Sale/Sharing | Opt-in required for third-party use | "Do Not Sell or Share" link mandatory |
| Response Timeline | Typically 30 days | 45 days (extendable to 90) |
| Right to Delete | "Right to be forgotten" | Right to request deletion |
| Enforcement Authority | National Data Protection Authorities | California Privacy Protection Agency & Attorney General |
How These Regulations Affect CRO
These legal differences have a direct impact on how you implement ethical CRO practices. To comply with CCPA, your website must include a visible "Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information" link, allowing California users to opt out of behavioral advertising .
Data retention policies also play a crucial role. GDPR requires you to collect only the data you need and delete it once it’s no longer necessary. CCPA, on the other hand, mandates that businesses disclose retention periods at or before the point of data collection and update their privacy policies annually . If a user requests data deletion, you must not only remove their data but also inform third-party processors to do the same.
For CRO tools, incorporating Global Privacy Control (GPC) is a must. CCPA-covered businesses are required to honor GPC signals as valid opt-out requests. Both GDPR and CCPA also aim to eliminate dark patterns – manipulative interface designs that trick users into consenting to tracking they might otherwise reject .
"The impetus behind the GDPR was to give private individuals more control over how their personal data are collected and processed." – Richie Koch, Managing Editor, GDPR.eu
When conducting A/B testing, it’s vital to tailor consent flows to your audience. For EU users, tracking can only proceed after they opt in. For California users, tracking is permissible unless they opt out, but an easy-to-find opt-out link is essential. These considerations are key when choosing tools that align with ethical data practices.
sbb-itb-6e49fcd
Using PageTest.AI for Ethical CRO
How PageTest.AI Supports Ethical Practices
PageTest.AI takes its ethical responsibilities seriously, embedding compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA into its core operations. Every aspect of its data processing is designed to align with these standards, ensuring transparency and accountability.
"We process your information only when we have a valid legal reason to do so." – PageTest.AI Privacy Policy
The platform follows the principle of data minimization, avoiding the collection of unnecessary personal details. For example, during A/B testing of headlines or CTAs, it tracks only key metrics such as clicks, engagement levels, time spent on a page, and scroll depth. Sensitive or irrelevant data is never collected. Additionally, PageTest.AI anonymizes user data automatically after tests are completed or if an account is closed. Users also have full control over their information, with the ability to access, correct, or delete their data whenever needed.
Simplifying Compliant Data Collection
PageTest.AI makes ethical data management straightforward with its no-code setup, allowing marketers to implement compliant CRO practices with ease. Through its user-friendly interface, you can test site elements, create AI-driven content variations, and monitor performance metrics – all while adhering to privacy laws. To ensure full compliance, it’s essential to integrate PageTest.AI scripts with a Consent Management Platform (CMP), so no data is collected before users give explicit consent. For California residents, the platform provides clear options to opt out of data sharing and targeted advertising.
"No purpose in this notice will require us keeping your personal information for longer than the period of time in which users have an account with us." – PageTest.AI Privacy Policy
The platform simplifies regular data audits by only collecting information directly from users – either through voluntary input or automatic service usage. It never pulls data from third-party sources, ensuring that only the essentials are gathered. To further support ethical practices, PageTest.AI provides clear privacy documentation, including a "Summary of Key Points", making it easy for marketers to understand user rights and data handling procedures. By integrating these features, PageTest.AI strengthens its commitment to ethical and compliant CRO practices.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Examples of Unethical Practices
Marketers occasionally cross ethical lines, particularly when it comes to privacy. Take Google, for instance. Back in January 2019, France’s data protection authority (CNIL) fined the tech giant €50 million for failing to clearly explain how user data was being used for ad personalization. The issue? Google’s consent process was too vague, a misstep that highlights how unclear privacy policies can lead to hefty fines.
British Airways found itself in a similar predicament. In October 2020, the UK Information Commissioner’s Office hit the airline with a $26 million fine due to a 2018 data breach. This breach exposed sensitive personal and financial details of over 400,000 customers and went unnoticed for two months because of insufficient security measures.
Amazon Alexa also faced scrutiny. Research from three U.S. universities revealed that between 2021 and 2022, Alexa devices collected sensitive voice and biometric data, sharing it with as many as 41 advertising partners – without adequately informing users.
Another common error involves sending personally identifiable information (PII) to analytics platforms, such as Google Analytics 4. This often happens when marketers use the GET method for form submissions instead of POST. As a result, sensitive details like emails, phone numbers, and names end up in URL parameters, making them accessible to analytics tools.
These examples show how unethical practices not only result in legal consequences but also erode the trust that ethical conversion rate optimization (CRO) aims to build. Below are actionable steps to avoid such pitfalls.
Do’s and Don’ts for Ethical CRO
To steer clear of these missteps, here are some best practices for ethical CRO:
- Do use the POST method for form submissions and replace personal identifiers with unique user IDs. This keeps sensitive data out of third-party tracking tools.
- Don’t use pre-checked boxes or bundle consent requests together. Each purpose for data collection should have its own clear, explicit opt-in. Both "Accept" and "Reject" buttons must be equally visible.
- Do collect only the bare minimum of data necessary to meet your business goals. As Karan Sharma, a data ethics expert, puts it:
"Ethical data collection is not a checklist item. It is the foundation of trustworthy, long-term data operations".
- Don’t engage in cloaking, which involves showing different content to search engine bots than to real users. This can lead to removal from search indexes. Also, avoid using behavioral nudges that may mislead users into making decisions based on deceptive signals.
- Do prioritize security by using SSL certificates, encrypting data both in transit and at rest, and implementing two-factor authentication. Websites with SSL certificates, for example, enjoy a conversion rate of 3.9%, compared to 2.3% for those without.
Conclusion
Ethical data collection isn’t just about following regulations – it’s the cornerstone of building trust in conversion optimization. In 2026, trust has become the deciding factor for whether users choose to engage with your site. As Paul Wilkins from Conversio aptly states:
"Trust is a fragile commodity, hard won and easily lost."
By following the checklist’s recommendations, the focus shifts from coercion to creating a seamless experience that respects user autonomy. Instead of pushing users into decisions they aren’t ready for, modern optimization removes barriers, allowing users to engage on their terms. Collecting only the necessary, anonymized data while offering clear opt-out options demonstrates a strong commitment to earning and maintaining user trust.
Incorporating trust signals, like regulatory badges, has been shown to increase conversion rates by 15–25% in sensitive scenarios. Beyond immediate results, these practices foster loyalty, creating a foundation for sustainable, user-centric growth.
Tools like PageTest.AI make it easier to uphold these principles. By embedding privacy-by-design features such as automatic data anonymization, compliance alerts, and transparent opt-out options, it ensures you can run effective A/B tests without compromising user privacy. Its no-code approach allows you to focus on crafting meaningful user experiences while the platform handles the technical side of compliance.
FAQs
What is the difference between GDPR and CCPA when it comes to data collection for CRO?
The main distinction between GDPR and CCPA in data collection boils down to how consent is handled and the overall scope of each regulation. GDPR, which governs businesses dealing with data from EU residents, requires prior opt-in consent – meaning users must give explicit permission before their data can be collected or used. In contrast, CCPA, which applies to businesses interacting with California residents, operates on an opt-out model. Here, data collection happens by default, but consumers have the right to opt out of tracking, data sharing, or selling.
Another key difference lies in focus. GDPR leans heavily on transparency and securing consent for specific purposes, ensuring users know exactly how their data will be used. CCPA, meanwhile, is centered on empowering consumers with rights to access, delete, or opt out of data sharing. These regulatory nuances require marketers to adjust their data collection approaches carefully, ensuring compliance while upholding ethical standards in their efforts to optimize conversions.
How can businesses ethically collect only the data they need for CRO?
To collect data ethically for conversion rate optimization (CRO), businesses should focus on data minimization – only gathering the information absolutely necessary to enhance user experience and improve site performance. Always make sure to get clear, explicit consent from users, clearly explaining how their data will be used. Avoid any practices that might come across as deceptive or manipulative.
Being upfront with users is essential. Let them know exactly what data you’re collecting, why you need it, and offer them the ability to manage their preferences. By adhering to privacy guidelines like GDPR and incorporating privacy by design principles, you can respect user rights while still achieving your optimization goals. Transparency builds trust and ensures ethical data practices.
How can data be anonymized ethically during conversion rate optimization (CRO)?
To handle data ethically during CRO, it’s essential to anonymize it by removing or masking anything that could reveal someone’s identity. This includes obvious details like names and addresses, as well as less direct information such as unique demographic characteristics or specific behaviors.
It’s equally important to ensure that any data shared externally is fully de-identified, making it impossible to trace back to individuals. Taking the time to perform a thorough risk assessment and adhering to recognized anonymization practices not only safeguards user privacy but also builds trust and ensures compliance with legal and ethical guidelines.
Related Blog Posts
say hello to easy Content Testing
try PageTest.AI tool for free
Start making the most of your websites traffic and optimize your content and CTAs.
Related Posts

 26-01-2026
26-01-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
Category Page Layouts That Boost SEO
Optimize category pages with clear hierarchies, concise above-fold copy, mobile-first layouts, schema, image optimization and pagination to increase traffic.

 24-01-2026
24-01-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
Statistical Significance in Multivariate Tests
How to get reliable results from multivariate tests using fractional designs, statistical corrections, variance reduction, and AI automation.

 22-01-2026
22-01-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
AI in Real-Time Performance Monitoring
AI-powered real-time monitoring uses predictive analytics, adaptive anomaly detection, and automation to cut downtime, boost efficiency, and improve conversions.
