Statistical Significance in Multivariate Tests

Statistical Significance in Multivariate Tests
 24-01-2026 (Last modified: 26-01-2026)
24-01-2026 (Last modified: 26-01-2026)
Statistical significance ensures that test results are reliable and not due to random chance. This concept is crucial for making informed decisions during website testing. Multivariate testing (MVT) analyzes multiple elements simultaneously but demands more traffic and careful statistical handling compared to multivariate testing vs A/B testing comparisons.
Key takeaways:
- A/B Testing: Compares two versions of one element; requires less traffic.
- Multivariate Testing: Tests multiple elements at once; needs higher traffic to detect reliable patterns.
- Statistical tools like p-values and corrections (e.g., Bonferroni) help reduce errors in tests with many variables.
- AI-powered tools (e.g., PageTest.AI) simplify MVT by automating tasks like creating combinations, tracking metrics, and calculating significance.
For small businesses, affordable AI tools make MVT more accessible, even with limited traffic or resources. The right strategies – like fractional factorial designs and variance reduction techniques – can optimize testing efforts while ensuring dependable results.
“We’ve seen teams call a winner after a few days because one variant ‘felt better’. In practice, those early gains often disappeared once the test reached proper statistical significance.” Ian Naylor, Founder of PageTest.ai
A/B Testing & Statistical Significance – 4 Steps to Know How to Call a Winning Test
sbb-itb-6e49fcd
Common Challenges in Achieving Statistical Significance
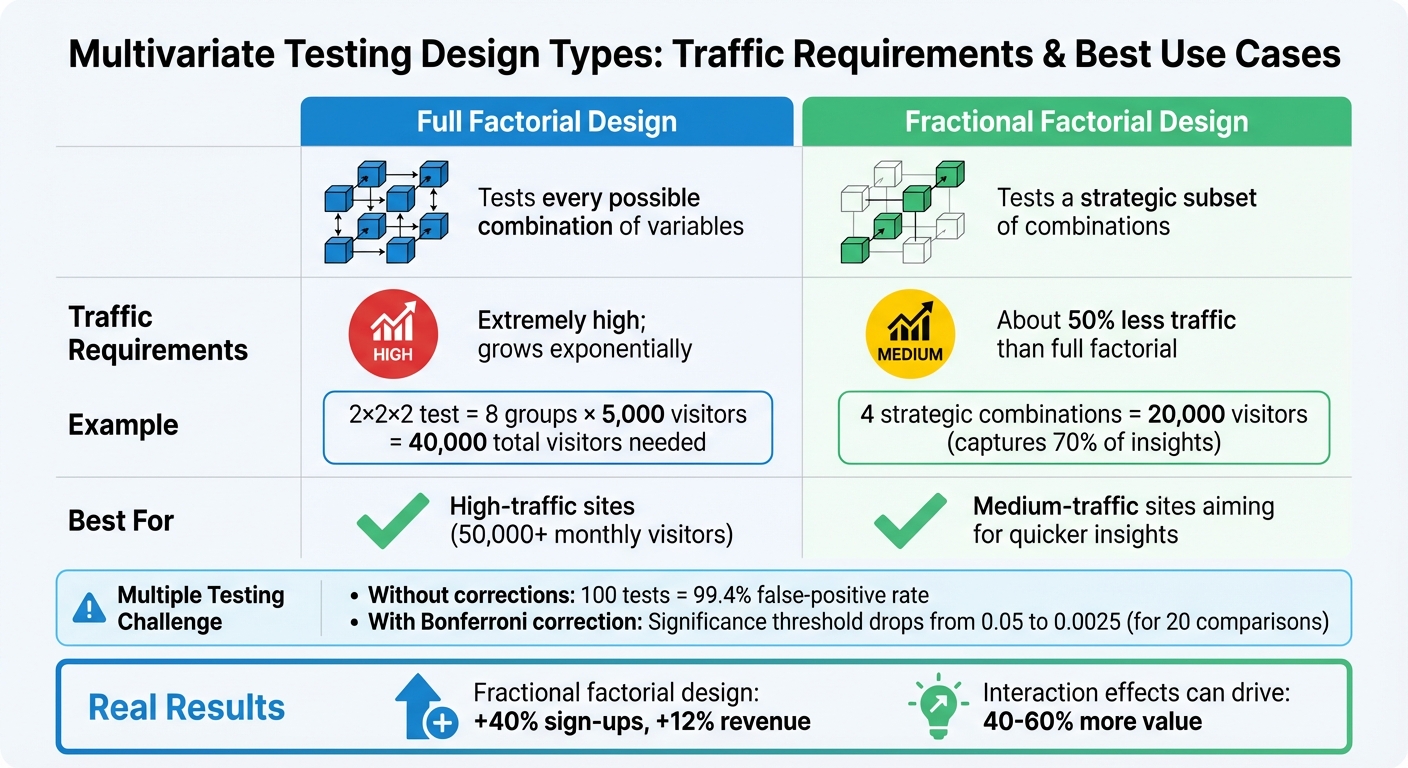
A/B Testing vs Multivariate Testing: Traffic Requirements and Design Comparison
When it comes to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO), statistical significance plays a crucial role, but achieving it isn’t always straightforward – especially with multivariate tests. These tests, while offering valuable insights, come with their own set of hurdles. The biggest challenge? The traffic demands soar as you introduce more variables. What works for a simple A/B test can crumble under the weight of testing multiple elements at once. Let’s break down the key issues.
Problem: Large Sample Size Requirements
In a typical A/B test, you’re working with just two groups. But switch to a 2×2×2 multivariate test, and you suddenly have 8 groups. Each combination requires at least 5,000 visitors, meaning you’ll need a whopping 40,000 visitors to run the test properly.
| Design Type | Description | Traffic Requirements | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Factorial | Tests every possible combination of variables | Extremely high; grows exponentially | High-traffic sites (50,000+ monthly visitors) |
| Fractional Factorial | Tests a strategic subset of combinations | About 50% less traffic than full factorial | Medium-traffic sites aiming for quicker insights |
The situation becomes even trickier when you apply strict significance thresholds. To avoid false positives, methods like the Bonferroni correction are often used. This technique lowers the alpha level by dividing it by the number of comparisons. For example, if you’re running 20 comparisons, the threshold drops from 0.05 to 0.0025, making it far harder to pinpoint a statistically significant result.
Problem: Multiple Testing and False Positives
Testing numerous variants at once introduces the “multiple comparisons problem.” Each additional test increases the likelihood of finding a result that looks significant but is actually just random noise. Priya Ranganathan from the Tata Memorial Centre explains:
“Multiple testing refers to situations where a dataset is subjected to statistical testing multiple times… This amplifies the probability of a false-positive finding”.
To put it in perspective, running 100 tests without adjustments could result in a false-positive rate as high as 99.4%. Without proper statistical corrections, you risk falling into the trap of data dredging – analyzing so many comparisons that false positives become almost unavoidable.
Problem: Identifying Interaction Effects
One of the main goals of multivariate testing is to uncover interaction effects – cases where the combined impact of two variables is different from the sum of their individual effects. But identifying these interactions requires significantly more data than measuring main effects alone.
For example, while a red button might increase conversions by 3%, pairing it with an urgent headline could overwhelm users and actually reduce conversions. Detecting these nuanced interactions requires advanced methods like ANOVA or G-tests, and each combination needs enough traffic to yield reliable insights. Without sufficient data, you risk missing out on these key findings – findings that could potentially reveal how elements work together to drive 40–60% more value.
Solutions for Overcoming Statistical Challenges
Multivariate testing can still deliver valuable insights when designed thoughtfully and paired with the right statistical methods. By optimizing your approach, you can minimize traffic requirements while ensuring your results remain reliable. Here’s how to approach it effectively.
Use Fractional Factorial Designs
Testing every possible combination of variables can be overwhelming and traffic-intensive. Instead, fractional factorial designs allow you to test selected combinations strategically, focusing on the most critical insights. These designs emphasize main effects (how individual variables perform) and two-way interactions (how variables work together in pairs), while skipping higher-order interactions that rarely contribute meaningful insights.
For example, in a three-variable test, you could test just four strategic combinations to capture about 70% of the insights while using only 50% of the traffic. Real-world results back up this approach: one campaign using fractional factorial designs increased sign-ups by over 40%, while another saw a 12% revenue boost. These outcomes highlight how targeted testing can yield impressive returns.
“From what i’ve seen, multivariate tests surface interactions you’d never predict. For example, a headline that underperformed on its own suddenly became the top performer when paired with a different CTA. This is what makes testing exciting!” Becky Halls, Strategist at PageTest.ai
Apply Statistical Adjustments to Reduce False Positives
When running multiple comparisons, you risk encountering false positives if you don’t adjust your significance thresholds. A simple solution is the Bonferroni correction, which divides your significance level (typically 0.05) by the number of comparisons. For example, testing 10 variants would lower your threshold to 0.005.
However, Bonferroni’s strictness can lead to missed opportunities. If detecting true improvements is more important than avoiding false positives, consider the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. This method controls the False Discovery Rate (FDR) rather than the Family-Wise Error Rate (FWER), making it less conservative and better suited for identifying real effects. As the Statsig Team explains:
By allowing a small proportion of false positives, the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure is less conservative than the Bonferroni correction and more powerful in detecting true positives.
For even more precision, advanced resampling methods like Romano-Wolf can further improve your ability to detect true effects. These methods achieve approximately 87% detection accuracy compared to Bonferroni’s 78.5%, all while maintaining a 5% error rate. Your choice of method should align with your priorities: use Bonferroni when avoiding false positives is critical, and Benjamini-Hochberg or Romano-Wolf when identifying true effects is more important.
“We’ve found that understanding statistical significance matters far more in multivariate tests than simple A/B tests. Without it, teams don’t end up optimizing for the right outcomes.” Becky Halls Strategist at PageTest.ai
Optimize Sample Size and Reduce Variance
Speed up your tests by selecting an appropriate minimum detectable effect (MDE). A larger MDE reduces the required sample size but increases the likelihood of missing smaller improvements. Industry benchmarks typically set alpha at 5% (95% confidence) and beta at 20% (80% power).
Variance reduction techniques like CUPED (Controlled-experiment Using Pre-Experiment Data) can also make a big difference. By leveraging historical data to reduce metric noise, CUPED can shorten test durations by 20% to 80%. Additionally, choosing primary metrics with lower natural variance based on past data and running tests for at least one full week can help account for fluctuations caused by day-of-week behavior.
Paul Markowitz, Principal at Bain & Company, offers a key insight into sample size efficiency:
The drivers of sample size do not include factors that we normally expect. We can keep adding attributes and test cells without affecting the total sample size needed.
In other words, your total sample size depends on the attribute with the most levels, not the total number of combinations. This makes multivariate testing (MVT) far more efficient than many marketers realize. With these refined methods, you’ll be well-positioned to incorporate AI-powered tools into your multivariate testing strategy effectively.
Using AI-Powered Tools for Multivariate Testing
AI-powered tools have simplified the often complex process of multivariate testing. Traditionally, running these tests required manually handling intricate statistical calculations and validating results. AI platforms take over these tasks, automating everything from calculating p-values and confidence intervals to managing test variations and pinpointing the best-performing combinations.
How PageTest.AI Tackles Multivariate Testing Challenges
PageTest.AI is designed to overcome the hurdles that make multivariate testing difficult for many teams. With its no-code setup, you can launch tests in just a few minutes using a Chrome extension. Whether you’re testing headlines, CTAs, or product descriptions, the platform’s AI-generated content variations create multiple options automatically.
The tool tracks key performance metrics like clicks, engagement, time on page, and scroll depth, providing a comprehensive view of how each combination performs. It also includes built-in statistical significance calculators that notify you when your data is robust enough to make reliable decisions. This eliminates two common pitfalls: stopping tests too soon (when results are still inconclusive) or running them longer than needed (wasting time and resources).
PageTest.AI’s advanced AI engines incorporate sequential testing and false discovery rate control, enabling faster and more accurate results compared to traditional methods. As Pierce Porterfield from Marpipe notes:
Statistical significance is an important hallmark of data validity… But the old 50-conversion benchmark isn’t always possible or necessary.
Additionally, the platform features real-time confidence meters that clearly indicate whether performance changes are due to chance (0–55% confidence) or represent measurable improvements (80–100% confidence). For teams with limited resources, these capabilities make AI-driven testing a game-changer.
Why AI-Driven Testing Works for Small Businesses
Small businesses often lack the traffic volume and data science expertise needed for traditional multivariate testing. AI-driven tools like PageTest.AI bridge this gap by automating the management of complex tests. For example, if you’re testing 2 headlines, 2 images, and 2 buttons, the platform automatically creates and manages all 8 possible combinations.
PageTest.AI’s affordability also makes it accessible. The Startup plan costs just $10 per month, covering 10,000 test impressions, 10 pages, and 10 tests. This is enough to detect meaningful changes, such as a 20% improvement, which typically requires around 2,500 users per variation.
Conclusion
Multivariate testing comes with its own set of hurdles – like managing sample size, handling multiple comparisons, and accounting for interaction effects. If these factors are ignored, it can lead to misleading results or missed opportunities to achieve conversion gains of 40–60%.
To navigate these challenges effectively, you can rely on strategies that simplify the process while ensuring accurate results. Approaches like fractional factorial designs and statistical adjustments, such as the Bonferroni correction or False Discovery Rate (FDR) control, help address traffic limitations and control error rates. These techniques strike a balance between reducing false positives and identifying meaningful improvements.
For teams working with tighter budgets or fewer resources, AI-powered platforms can take much of the heavy lifting off your plate. Tools like PageTest.AI automate critical tasks, including calculating sample sizes, applying sequential testing methods, and offering real-time confidence metrics. Starting at just $10 per month for the Startup plan, even small businesses can run advanced multivariate tests that were once reserved for enterprises.
A practical way to begin is by launching a 2×2 design on high-traffic pages, then scaling up as you collect reliable data. By blending efficient design methods, robust statistical controls, and cutting-edge AI solutions, you can streamline your testing process and maximize its impact – without unnecessary complexity or delays.
Leverage these strategies and tools to consistently refine your testing approach and drive meaningful conversion improvements.
Statistical Significance FAQs
How can small businesses run effective multivariate tests with low website traffic?
Small businesses with less website traffic can still pull off effective multivariate testing by honing in on strategies that make the most of their resources. The key? Focus on elements that directly impact conversions – think headlines, calls-to-action (CTAs), or product descriptions. By narrowing the scope, you’ll cut down the number of variations and the sample size needed, making it easier to reach reliable conclusions.
Tools like PageTest.AI can step in to streamline the process. These AI-powered platforms automatically generate and test variations, saving time and helping you make the most of limited traffic. Another smart move is to calculate your required sample size upfront. This way, you can ensure your results are dependable without stretching your resources too thin. With a thoughtful approach to variable selection and a bit of automation, even small businesses can uncover valuable insights and fine-tune their websites for better performance.
What’s the difference between full factorial and fractional factorial designs in multivariate testing?
Full factorial designs examine every possible combination of factors and their levels, offering a thorough look at both main effects and interactions. While this approach provides comprehensive results, it can demand significant resources, especially when dealing with numerous factors.
In contrast, fractional factorial designs analyze a smaller, carefully chosen subset of combinations. This method focuses on the most important effects, cutting down on time and resources. It’s a great choice when you’re looking for practical insights without the need to explore every single possibility.
How can AI-powered tools help achieve statistical significance in multivariate testing?
AI-driven platforms like PageTest.AI simplify and speed up the process of achieving statistical significance in multivariate testing. These tools can automatically create content variations, assess performance metrics, and dynamically adjust traffic distribution to focus on the best-performing options.
By handling these tasks, AI minimizes manual work, fine-tunes sample sizes, and delivers more precise and reliable outcomes. This empowers businesses to make informed, data-backed decisions more quickly and confidently.
Related Blog Posts
say hello to easy Content Testing
try PageTest.AI tool for free
Start making the most of your websites traffic and optimize your content and CTAs.
Related Posts

 10-03-2026
10-03-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
Real-Time Metrics for CRO: What to Track
Monitor CVR, CTR, bounce rate, time on page and cart abandonment in real time to spot drop-offs and improve conversions.
 09-03-2026
09-03-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
Ultimate Guide to Personalized Recommendation Testing
How to test and optimize AI-driven product recommendations—algorithms, metrics, A/B methods, no-code tools, and best practices to boost CTR, AOV, and conversions.

 07-03-2026
07-03-2026
 Ian Naylor
Ian Naylor
What Is AI Mobile User Clustering?
Explains how AI groups mobile app users by behavior, key algorithms, data preparation, and practical uses for personalization, churn prediction, and marketing.
